Stroke is a medical emergency. Call 911.
Stroke is a type of cardiovascular disease that affects the arteries leading to and within the brain. A stroke occurs when a blood vessel that carries oxygen and nutrients to the brain is either blocked by a clot or bursts. Time is critical in stroke treatment. The faster you are taken to an emergency room, the better your chance for a positive outcome.
Stroke strikes F.A.S.T.
Not sure whether a person's symptoms are a stroke? Act F.A.S.T. and quickly take these steps.
- Face – Ask the person to smile
- Arm – Ask the person to raise both arms
- Speech – Ask the person to speak a simple sentence
- Time – Difficulty or impossible to complete one or more of these tasks? Call 911 now!
If you experience or see someone with these warning signs, call 911 immediately:
- Sudden numbness or weakness of the face, arm, or leg (especially on one side of the body)
- Sudden confusion, trouble speaking, or trouble understanding speech
- Sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes
- Sudden trouble walking, dizziness, loss of balance or coordination
- Sudden unexplained, severe headache
What is a stroke?
Strokes are aptly referred to as a "brain attack." When there is an interruption of blood flow to the brain, either because of a clot or ruptured blood vessel, sudden brain damage occurs.
A person who is having a stroke requires immediate medical attention. The longer it takes to receive care, the more brain cells will die and the greater the risk of disability or even death.
Two types of stroke
Ischemic stroke is most common and accounts for 87 percent of strokes. Ischemic stroke is caused by a clot that prevents blood flow to the brain. The clot can either travel to the brain from another part of the body or can develop in an artery.
Hemorrhagic stroke is a second type of stroke which occurs when a blood vessel in the brain breaks or ruptures. Hemorrhagic stroke is less common, but it's more deadly.
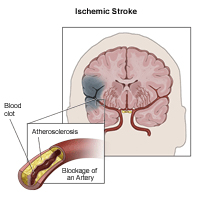
Ischemic stroke is caused by a clot in a blood vessel or artery.
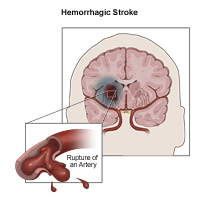
Hemorrhagic stroke is caused by a blood vessel in the brain that breaks.