Treatment Options
Inova offers both non-surgical and surgical treatments for ankle arthritis. Treatment is based on the results of the clinical history and examination, radiographs, and on the patient’s level of activity.
Non-Surgical treatments
Non-surgical treatments for ankle arthritis may include:
- Orthotics. Changing the alignment of your foot and/or ankle can improve the symptoms.
- Bracing. Braces can range from sports braces with laces and velcro to custom sturdy leather braces (Arizona brace)
- Physical therapy. Therapy is most effective when the arthritis is associated with instability. Therapy can improve the stability of the ankle by strengthening the muscles. Therapy can also help keep the ankle moving, which is important to maintain healthy joints
- Medications. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS), such as ibuprofen, naproxen, or meloxicam, may be prescribed to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Steroid Injections. Injecting a steroid into the ankle joint can significantly reduce inflammation in reduce pain.
- Activity Modification. Athletic individuals may alter the intensity and frequency of the sports that they play.
If non-surgical management fails to relieve pain adequately, surgery is something to discuss with your foot & ankle orthopedic surgeon. If symptoms are mild your surgeon may suggest using arthroscopic techniques to help you. Arthroscopy generally involves using a small camera to evaluate the ankle and small instruments to remove damaged cartilage and damaged tissue. Arthroscopic procedures use small incisions and are minimally invasive.
Surgical Treatments
When the arthritis is more advanced and pain continues, there are two common surgical treatments: ankle athrodesis (fusion) and total ankle arthroplasty (ankle replacement).
Ankle arthrodesis (fusion)
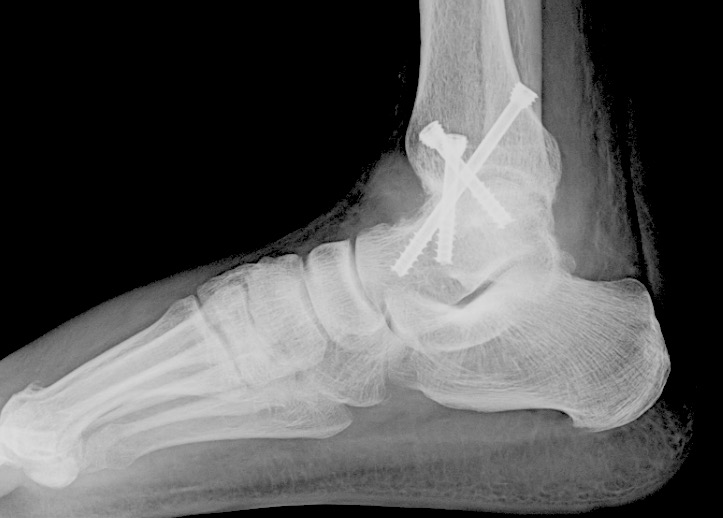 This surgical procedure involves growing the end of the tibia to the talus. In other words, the two bones that normally move in the ankle are transformed into one solid bone that no longer moves. This may be done arthroscopically or through a larger incision. Typically, screws alone or plates and screws are used to stabilize the fusion. Though the ankle does not move, the pain is dramatically reduced. You are likely at an increased risk of developing arthritis in other joints in your foot after this procedure. Your surgeon should discuss an ankle fusion with you, even if you are still a candidate for a total ankle replacement. Patients are nonweightbearing for at least 6 weeks after an ankle fusion in a splint or cast.
This surgical procedure involves growing the end of the tibia to the talus. In other words, the two bones that normally move in the ankle are transformed into one solid bone that no longer moves. This may be done arthroscopically or through a larger incision. Typically, screws alone or plates and screws are used to stabilize the fusion. Though the ankle does not move, the pain is dramatically reduced. You are likely at an increased risk of developing arthritis in other joints in your foot after this procedure. Your surgeon should discuss an ankle fusion with you, even if you are still a candidate for a total ankle replacement. Patients are nonweightbearing for at least 6 weeks after an ankle fusion in a splint or cast.
Total ankle arthroplasty (ankle replacement)
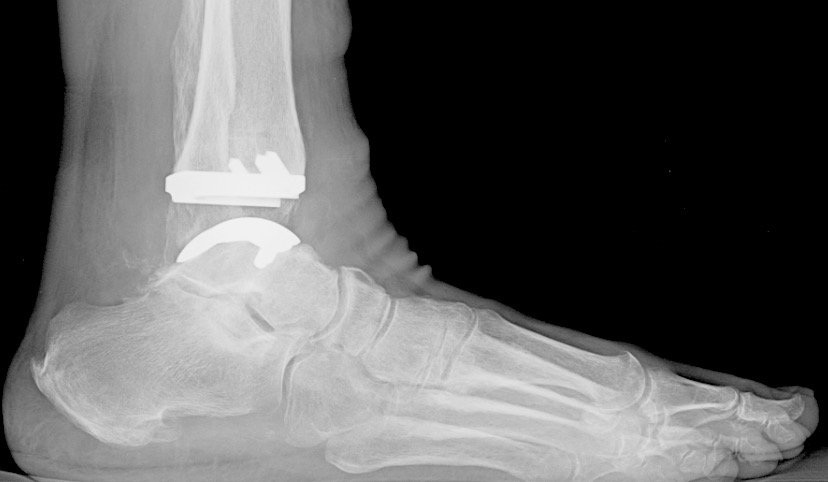 With this procedure, the motion is preserved at the ankle. This reduces the stress on the joints of the foot and may decrease the chances of developing arthritis. New implant designs have much better success rates than older designs. The ability of the new ankle joint to move up and down is considered an advantage over an ankle fusion. But like all joint replacements, an ankle replacement can wear out over time.
With this procedure, the motion is preserved at the ankle. This reduces the stress on the joints of the foot and may decrease the chances of developing arthritis. New implant designs have much better success rates than older designs. The ability of the new ankle joint to move up and down is considered an advantage over an ankle fusion. But like all joint replacements, an ankle replacement can wear out over time.
An ankle replacement is commonly performed under general anesthetic with a nerve block. The ankle is approached from the front or side. Bone is then cut and removed, allowing for placement of the metal and plastic components that re-create the ankle joint. The wound is then closed using stitches and a splint is applied. The patient is typically non-weightbearing for 2-3 weeks to allow for the incision to heal. Once the incision is healed, the patient can commonly bear weight in a boot and physical therapy is started. Recovery from an ankle replacement may take 6 to 12 months.
Who should not have an Ankle Replacement?
Not everyone is a good candidate for an ankle replacement. Ankles that are severely deformed or have had an infection in the past may do better with an ankle fusion. Patients with serious medical problems or blood flow problems are not good candidates for an ankle replacement either.
Who performs an Ankle Replacement?
Total ankle replacement surgery is a complicated procedure and should only be performed by an orthopedic surgeon or podiatrist who specializes in ankles and has performed many ankle replacements and fusions. There are risks with ankle replacement surgery including infection, healing problems and loosening or wearing out the metal and plastic. If these complications develop, additional surgery is usually needed. Meet our doctors 
For more information about the Ankle Replacement Program at Inova Fairfax Hospital, call our orthopedic nurse navigator at 703-776-2289.